Chicago, IL
2018: La Villita’s Nuestra Historia mural shows community history, cultural pride, and activism.
Courtesy of J. Weller and P. Morales Fuentes, UIC.
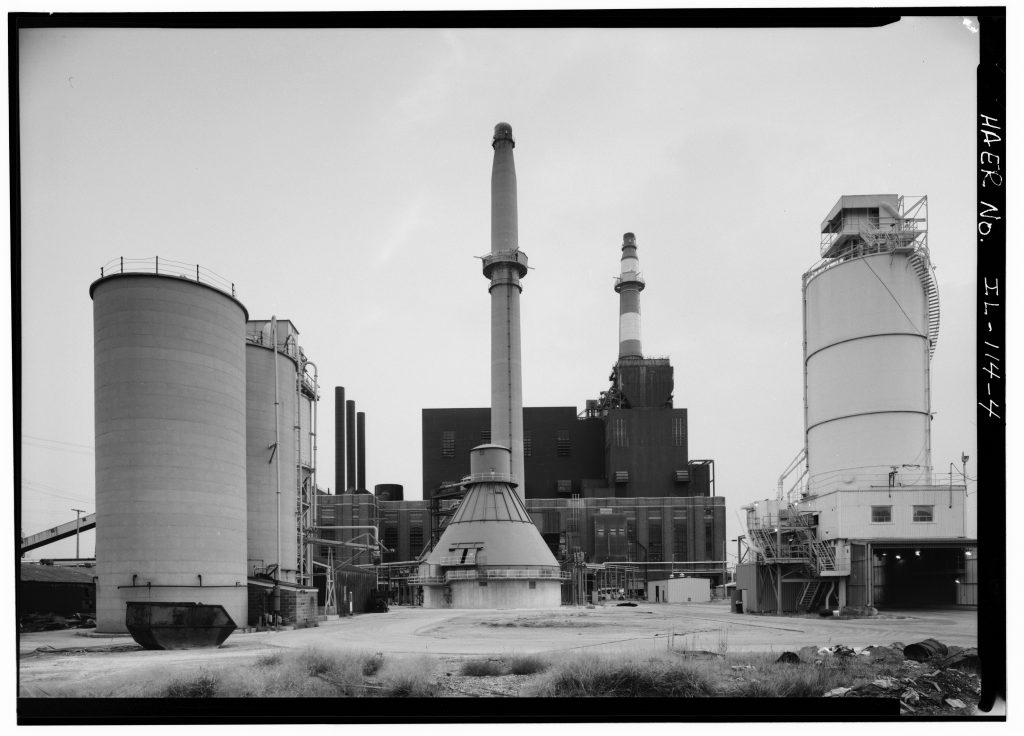

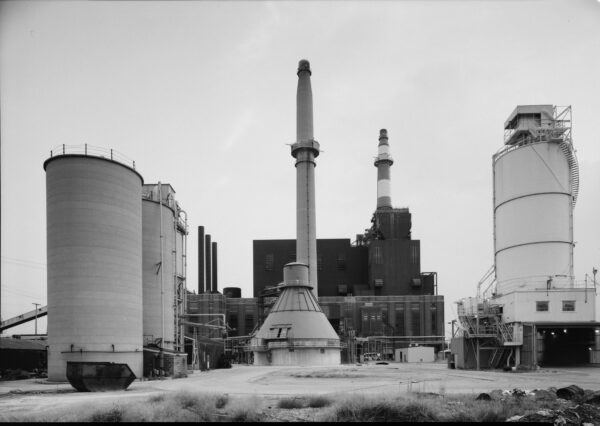
1987: The Crawford Generating Station closed in 2012 due to local grassroots activism.
Courtesy of Library of Congress.
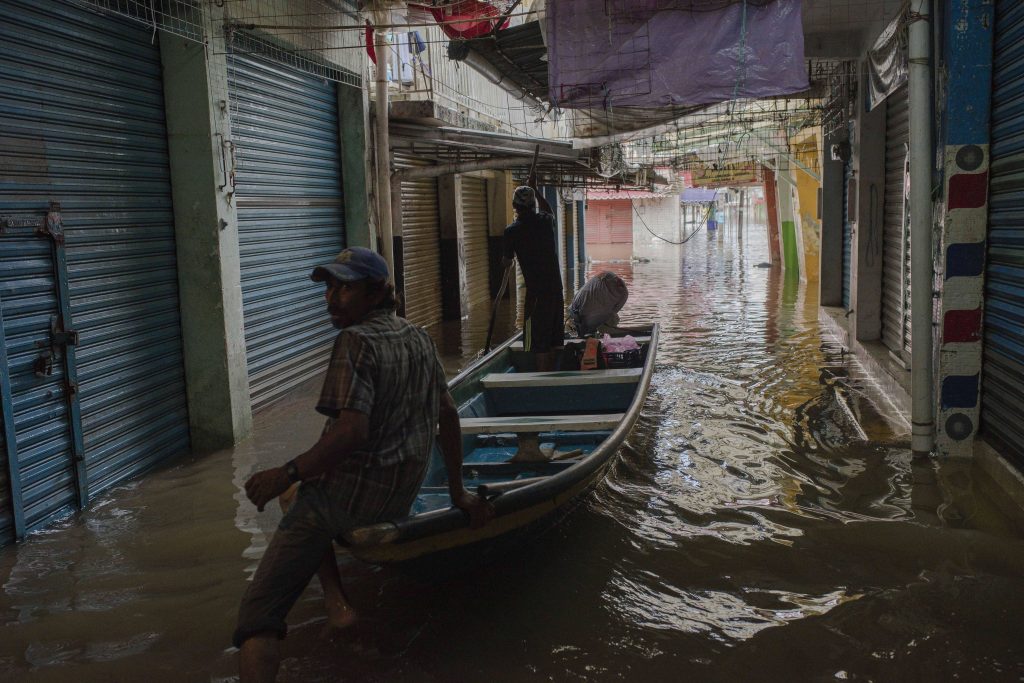

2018: Hurricane Willa caused many residents of Minatitlán, Mexico to relocate to the US.
Courtesy of Angel Hernandez/EPA-EFE/Shutterstock.
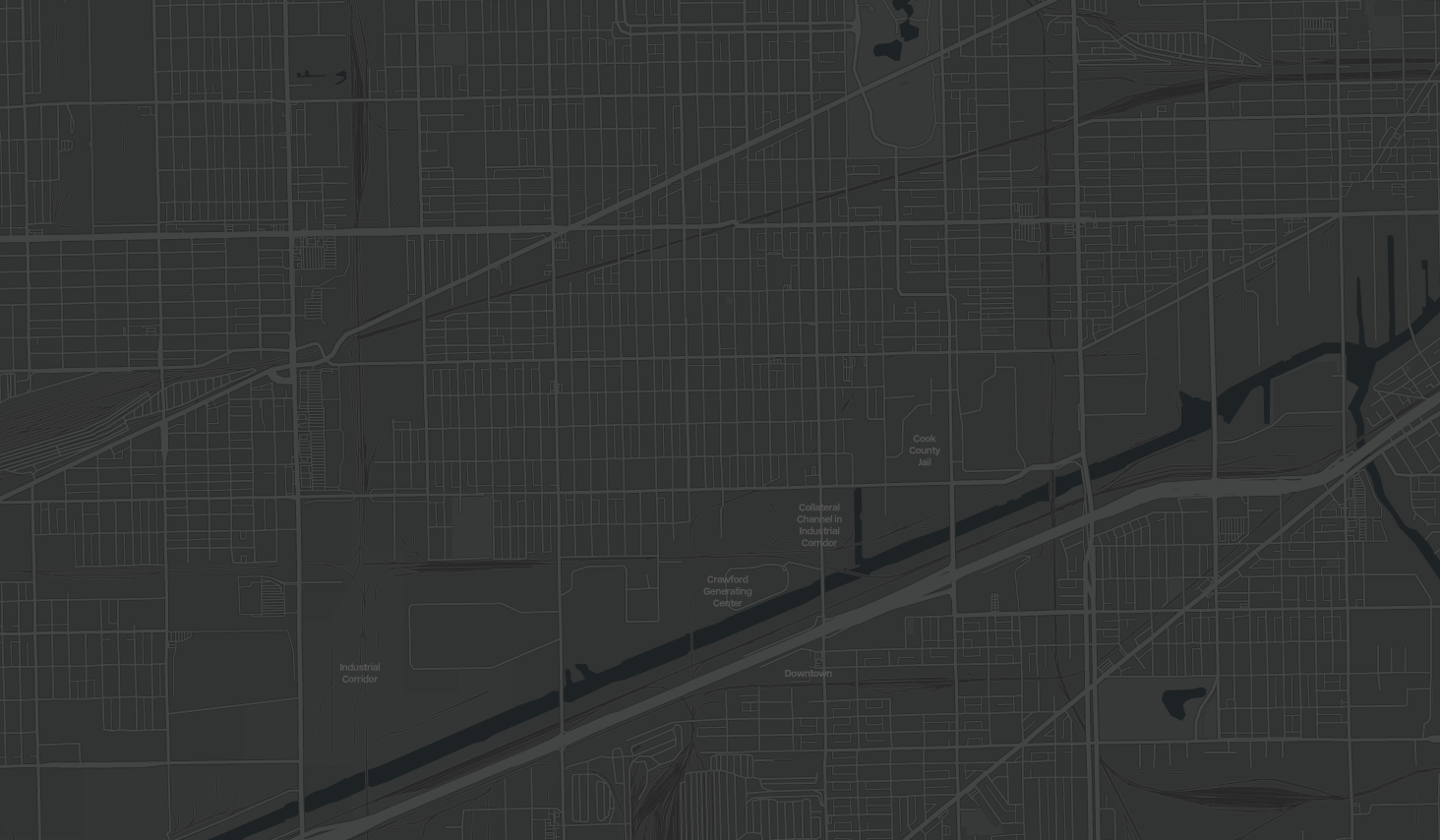
Living in Chicago’s 3rd largest industrial corridor, La Villita residents face systematic environmental racism worsened by corrupt politicians and corporations who prioritize profit over people’s well-being. Policing, criminalization of migrants, and land use for incarceration reveal how environmental injustice and immigration intersect in La Villita.
In the 1990s, the frequency of dramatic climate events and start of NAFTA increased the influx of migrants across Central America, Mexico, and the U.S. Settling in La Villita, immigrants confront toxic environments due to old zoning laws and discrimination linked to 19th century policing to protect industrialist interests.
Activists and scholars recognize social inequality as a major factor restricting climate change adaptation and forcing migration. In La Villita, campaigns like “Fight for the Right to Breathe,” youth development programs, community pride and resistance, along with environment-friendly practices are improving community life.
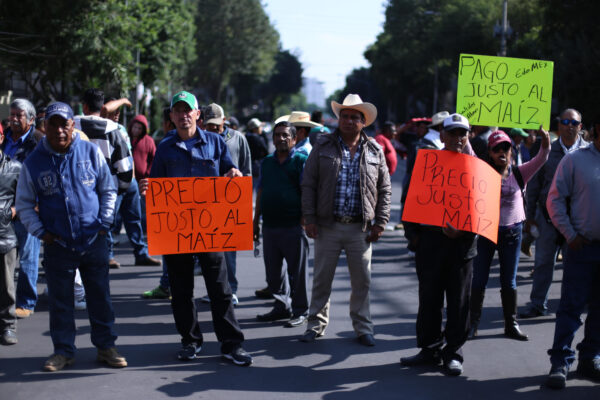
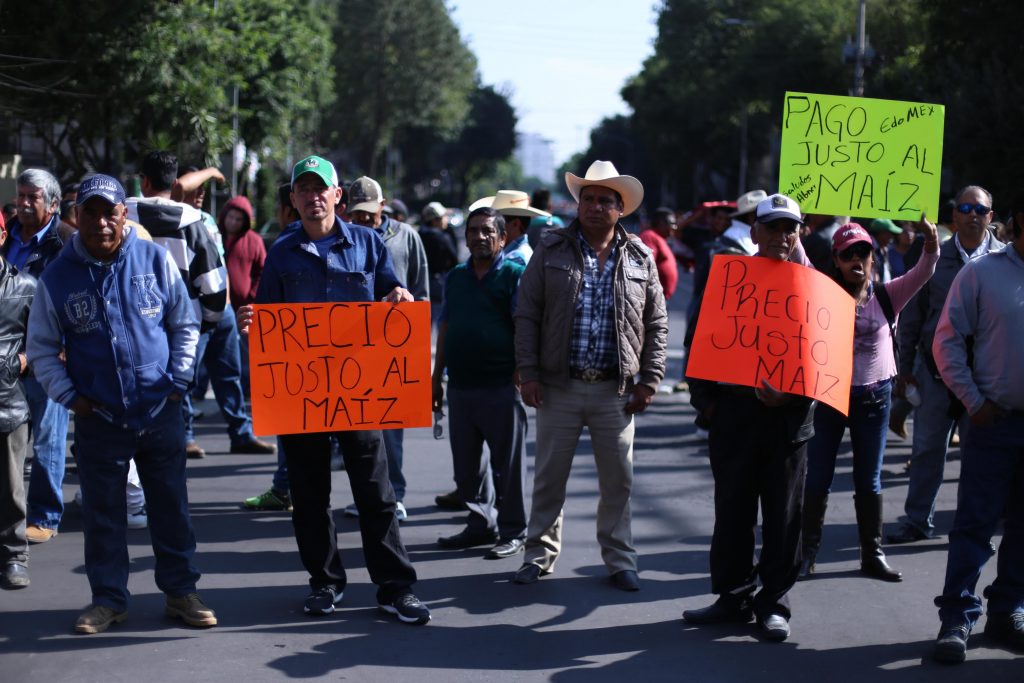











2017: Farmers in favor of leaving the North American Free Trade Agreement, Mexico City, Mexico.
Mario Guzman, EPA/Shutterstock.
2019: Journey through 26th Street shopping corridor
Courtesy of M.Insalata, UIC.
2019: Journey to collecting first voice experiences with Alianza Americas
Courtesy of M.Insalata, UIC.

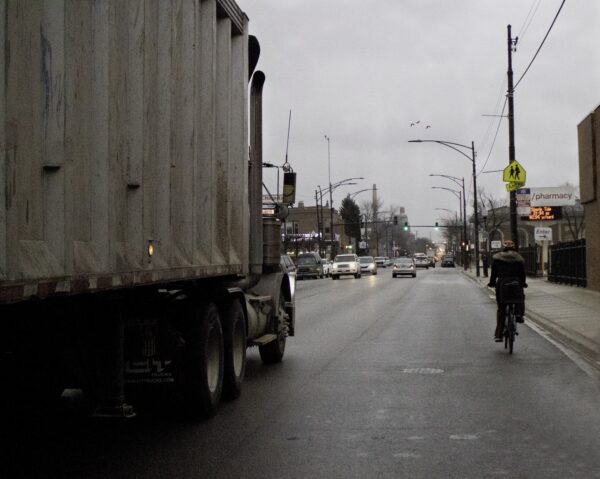
2019: Living in an industrial corridor means sharing the road with trucks every day in La Villita.
Courtesy of L. Cabrales and K. Solis, UIC.
2019: Journey to the Collateral Channel in the Industrial Corridor
Courtesy of M.Insalata, UIC.

2018: Im/Migration posters in La Villita are a reminder of rights and policing realities.
Courtesy of J. Weller, UIC.
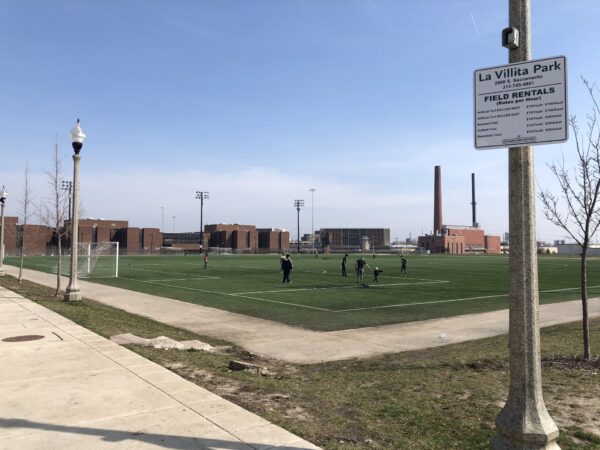
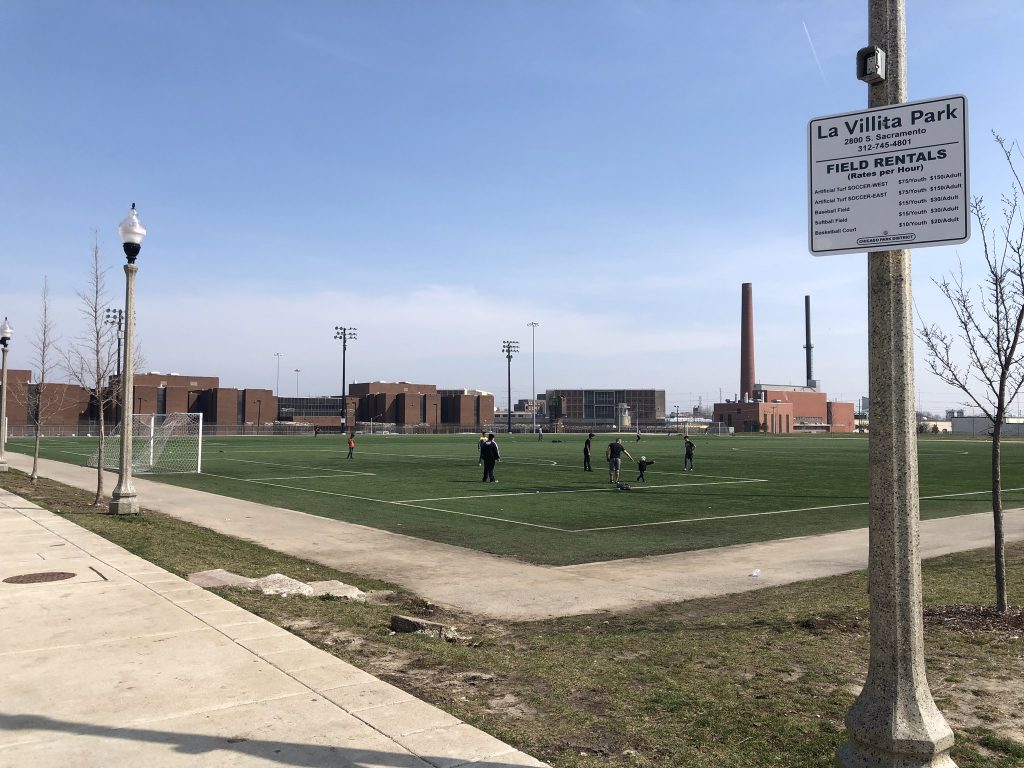
2019: Journey to La Villita Park, adjacent to Cook County Jail
Courtesy of M.Insalata, UIC.
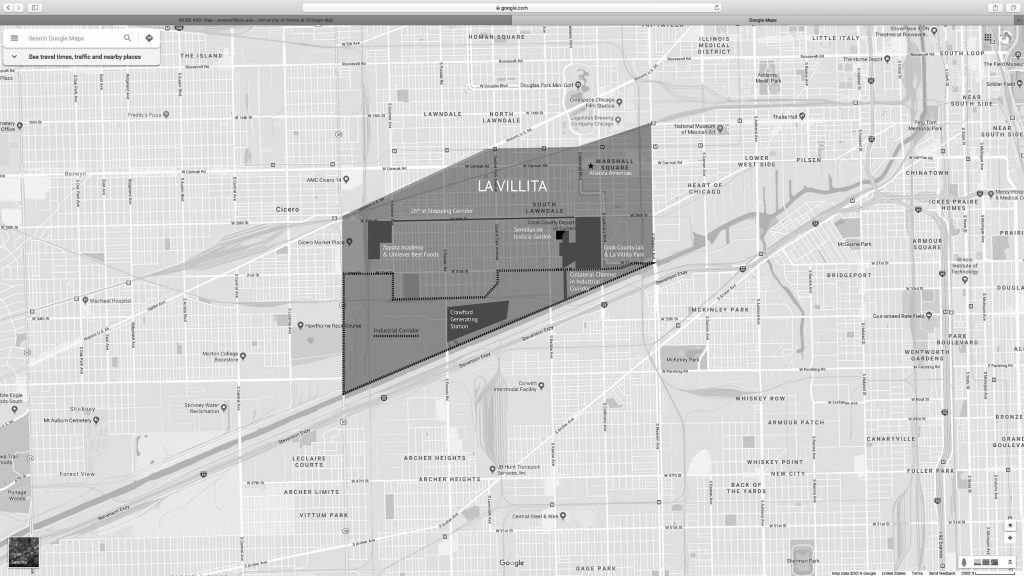
2019: La Villita’s 70,000 residents, mostly Latinx, live by major hazardous landmarks.
Courtesy of S. Lynn and P. Morales Fuentes, UIC.
2019: Journey through Zapata Academy and Unilever Best Foods
Courtesy of M.Insalata, UIC.
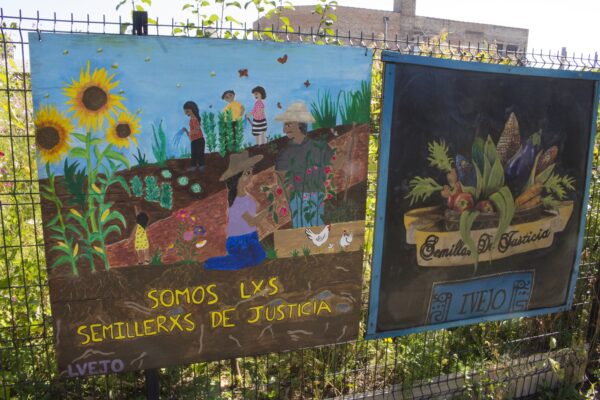
2019: Journey through LVEJO’s Semillas de Justicia Garden
Courtesy of M.Insalata, UIC.
2019: Journey to the Crawford Generating Station, Industrial Corridor
Courtesy of M.Insalata, UIC.
Our Point of View
During our yearlong course, we learned that environmental injustice is more than pollution. It involves social issues like immigration, policing, and economic inequities that favor the corporate elite. Our class of social justice newcomers, advocates, and activists come from across Chicagoland, including areas near industrial corridors. These diverse perspectives allowed us to listen critically and make connections with our community partners as we discovered the culturally based approaches they use to resist environmental discrimination.
—University of Illinois at Chicago
Few people will say they migrated due to climate change. But push a little harder and you hear many stories about drought, failed crops, devastating storms driving people to relocate to cities, where they encounter violence in many forms. Once living in the US, the deadly mix of environmental, economic and social injustices often repeats—via toxic exposure and gentrification. Alianza Americas works across borders on issues that affect immigrant communities. We joined this project to go deeper into the systemic environmental injustices faced by our members and the actions they take to fight back.
—Alianza Americas